Information Gathering - Web Edition Contents
Previous Section
DNS Tools¶
Below are some specialised tools designed to query DNS servers and extract valuable information:
| Tool | Key Features | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| dig | Flexible DNS Lookup tool that supports various query types (A, MX, NS, TXT, etc). | Manual DNS Queries, Zone Transfers (if allowed), Troubleshooting DNS Issues, and In-depth Analysis of DNS Records. |
| nslookup | Simpler DNS Lookup Tool, primarily for A, AAAA, and MX records. | Basic DNS queries, Quick Check of Domain Resolution, and Mail Server Records. |
| host | Streamlined DNS Lookup Tool with concise output. | Quick Checks of A, AAAA, and MX Records. |
| dnsenum | Automated DNS Enumeration Tool, Dictionary Attacks, Brute-Forcing, and Zone Transfers (if allowed). | Discovering Subdomains and gathering DNS Information efficiently. |
| fierce | DNS Reconnaissance and Subdomain Enumeration Tool with Recursive Search and Wildcard Detection. | User-Friendly Interface for DNS Reconnaissance, Identifying Subdomains, and potential Targets. |
| dnsrecon | Combines multiple DNS Reconnaissance techniques and supports various output formats. | Collecting Email Addresses, Employee Information, and Gathering Records for further analysis. |
| theHarvester | OSINT Tool that gathers information from various sources, including DNS Records (e.g. Email Addresses). | Collecting Email Addresses, Employee Information, and other associated data with a domain from multiple sources. |
Online DNS Lookup Tools¶
DNS Techniques¶
1) The Domain Information Groper (dig)¶
The dig (Domain Information Groper) is a flexible tool used for:
- Querying DNS Servers,
- Retrieving various types of DNS records.
Common Dig Commands¶
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| dig domain.com | Retrieves a default A Record lookup for the domain. |
| dig domain.com A | Retrieves the IPv4 Address (A Record) associated with the domain. |
| dig domain.com AAAA | Retrieves the IPv6 Address (AAAA Record) associated with the domain. |
| dig domain.com MX | Finds the Mail Servers (MX Records) responsible for the domain. |
| dig domain.com NS | Identifies the Authoritative Name Servers for the domain. |
| dig domain.com TXT | Retrieves any TXT Records associated with the domain. |
| dig domain.com CNAME | Retrieves the Canonical Name (CNAME) Record for the domain. |
| dig domain.com SOA | Retrieves the start of Authority (SOA) Record for the domain. |
| dig @1.1.1.1 domain.com | Specifies a Specific Name Server to query; in this case 1.1.1.1. |
| dig +trace domain.com | Shows the Full DNS Resolution Path. |
| dig -x 192.168.1.1 | Performs a Reverse Lookup on the IP Address, 192.168.1.1 to find the associated Host Name. A Name Server may need to be specified. |
| dig +short domain.com | Performs a short, and concise answer to the query. |
| dig +noall +answer domain.com | Displays only the answer section of the query output. |
| dig domain.com ANY | Retrieves all available DNS records for the domain. > Many DNS Records servers ignore ANY queries to reduce load and prevent abuse (i.e. RFC 8482). |
Caution: Some servers can detect and block excessive DNS queries. Use caution and respect rate limits. Always obtain permission before performing extensive DNS reconnaissance on a target.
Using Dig Groping DNS¶
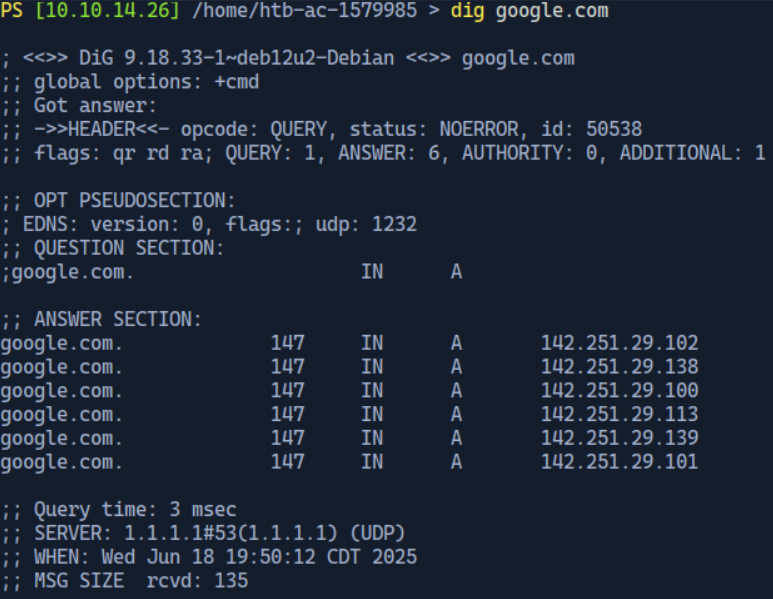
Example of Google.com dig command output.
| Dig Output Section | Example | Example Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Header | DNS Header:;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 16449:DNS Header Flags: ;; flags: qr rd ad; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0DNS Warning Flag: ;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available | DNS Header: Indicates the type of query (QUERY), the successful status (NOERROR) and a Unique Identifier (16449). DNS Header Flags: - qr: Query Response Flag which indicates this is a response. - rd: Recursion Desired Flag which means recursion was requested. - ad: Authentic Data Flag means the resolver considers the data authentic. The remaining numbers indicate the number of entries in each section of the DNS Response: - 1 Question, 1 Answer, 0 Authority Records, and 0 Additional Records. DNS Warning Flag: Indicating recursion was requested, but the server does not support it. |
| Question Section | IPv4 Address (A Record) for google.com;google.com. IN A | IPv4 Address (A Record): "What is the IPv4 address (A Record) for google.com?" |
| Answer Section | Answer To Query:google.com. 0 IN A 142.251.47.142 | Answer To Query: Indicates the ip address associated with google.com is 142.251.47.154.The 0 represents the TTL (Time-To-Live) indicating how long the result can be cached before being refreshed. |
| Footer | Time Query Took:;; Query time: 0 msecAnswer Obtained DNS Server & Protocol: ;; SERVER: 172.23.176.1#53(172.23.176.1) (UDP)Query Timestamp: ;; WHEN: Thu Jun 13 10:45:58 SAST 2024DNS Message Received Size: ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 54 | Time Query Took: Shows the time taken for the query to be processed and the response to be received (0 milliseconds). Answer Obtained DNS Server & Protocol: Identifies the DNS Server that provided the answer and the protocol used (e.g. UDP). Query Timestamp: Timestamp of when the query was made. DNS Message Received Size: Indicates the size of the DNS Message received (i.e. 54 Bytes). |
An opt pseudosection can sometimes exist in a dig query. This is a result of Extension Mechanisms for DNS (EDNS) which allows for additional features such as larger message sizes and DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) support.
Exercises¶
Q: Which IP address maps to inlanefreight.com?
A: 134.209.24.248
Q: Which domain is returned when querying the PTR record for 134.209.24.248?
A: inlanefreight.com
Q: What is the full domain returned when you query the mail records for facebook.com?
A: smtpin.vvv.facebook.com.