CO2412 Computational Thinking Contents
Lecture 10 - Object Based Modelling - Binary - Hexadecimal
Lecture 11 - Inheritance Based Structures & Interfaces.pdf
Inheritance Based Structures & Interfaces¶
Class Hierachies¶
In a football a Player class may have a number of attributes:
- Age
- Weight
- Height
The class may also have methods such as:
- Pass
- Tackle
Sub-classes to the Player class can also be identified where different behaviours will be needed. Some identified sub-classes include: Forward and Defender.
Abstract Classes¶
A Player serves as a parent class for the Forward and Defender.
It would serve no purpose to declare an object of the type Player. As such Player becomes an abstract class, which is a class without a constructor.
In UML Abstract Classes are identified by italics in the name.
Class Diagram¶
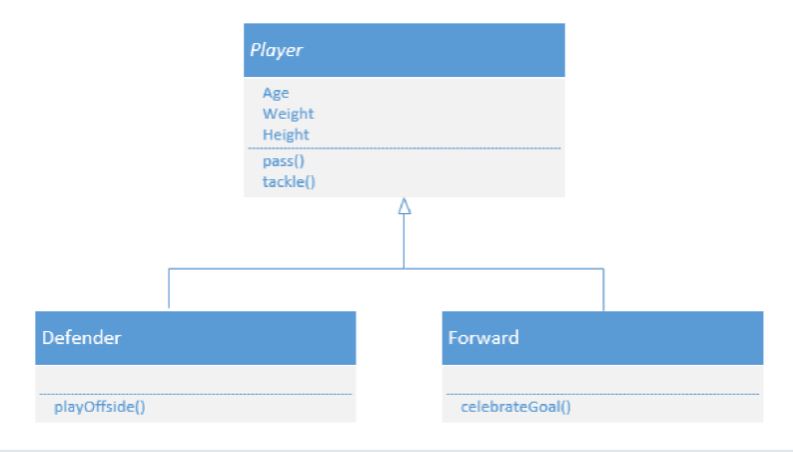
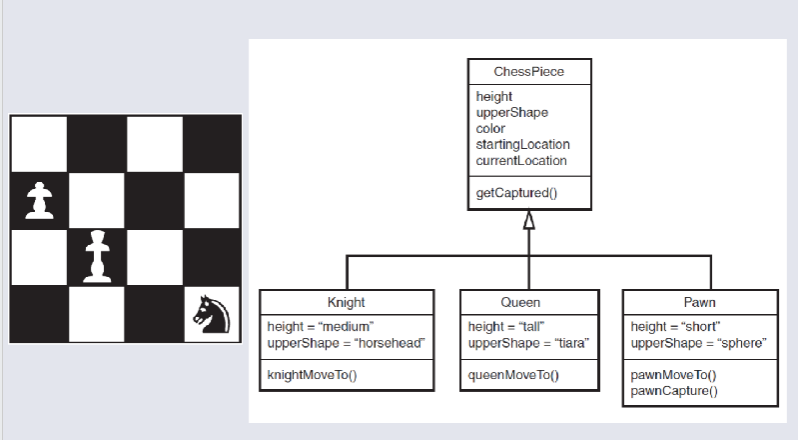
Class Diagrams give general defining information.
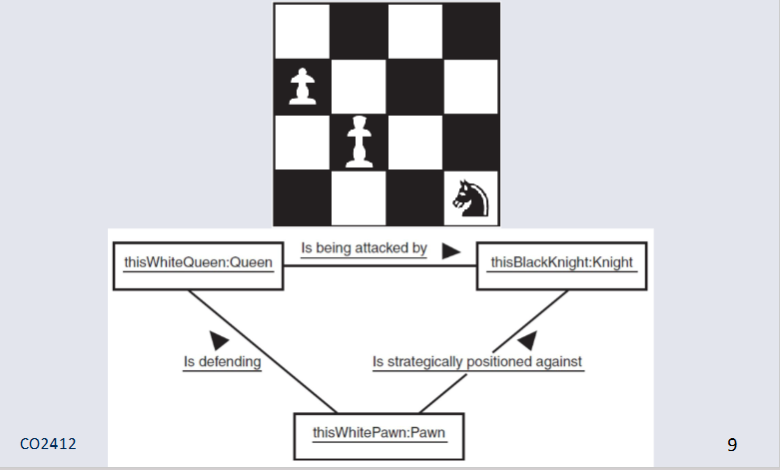
An Object diagram gives information about specific class instances.
Class Diagram Chess Board Example¶
Object Diagram Chess Board Example¶
Interfaces & Implementations - Component-Based Design¶
A sub-system with a clear interface providing a service.
Don't need to understand the implementation to use it.
If requirements aren't met, components won't work.
Abstraction¶
Interface defines the key features of the component.
Don't need to know the details of it's internal workings.
Ideally internal details are encapsulated so they cannot be changed.
Encapsulation & Information Hiding¶
Software Engineering is about managing complexity.
Breaking an application down into its base components and interacting through well-defined interfaces, and changing the internals increases the complexity.
Uses Setters & Getters to get encapsulated information.
Only reveal essential data information.
e.g. hiding implementation details (like authentication credentials)
Advantages¶
Reduces complexity
Easier to understand and maintain
Separation of concerns:
- User doesn't care how its implemented only how it works
- Coder cares how it works and ensures it is reusable in multiple programs
Preventing malicious or accidental damage.
Summary¶
An interface defines the methods to be provided by a class and can be implemented through different classes. Supports Abstraction and Encapsulation.
Class implements an interface by providing its methods and hides its implemental and internal data structures.
Classes/Functions avoid repeating the same code.
Generics
- Avoids duplication of code to handle different types.